1-3: These questions are about an arctic food web: |
Cmglee c.c. BY-SA 3.0 |
|||||||||||||||
1. Using the food web above, what is the mode of nutrition of the Carnivorous Zooplankton?
|
||||||||||||||||
2. Using the food web above, determine the different trophic levels of an Arctic Cod.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
3. In the food web above, determine the main energy transfers for phyto-plankton and herbivorous zooplankton.
|
||||||||||||||||
4. In most terrestrial ecosystems what happens to each trophic level as you move through a food chain?
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
5. Which of the following biomes would most likely accumulate the greatest biomass through primary production by autotrophs?
| Ville Koistinen c.c. BY-SA 3.0 |
|||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
6.What trends are shown in the Keeling Curve?
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
7. Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems. Which of the following provides decomposers with energy?
|
||||||||||||||||
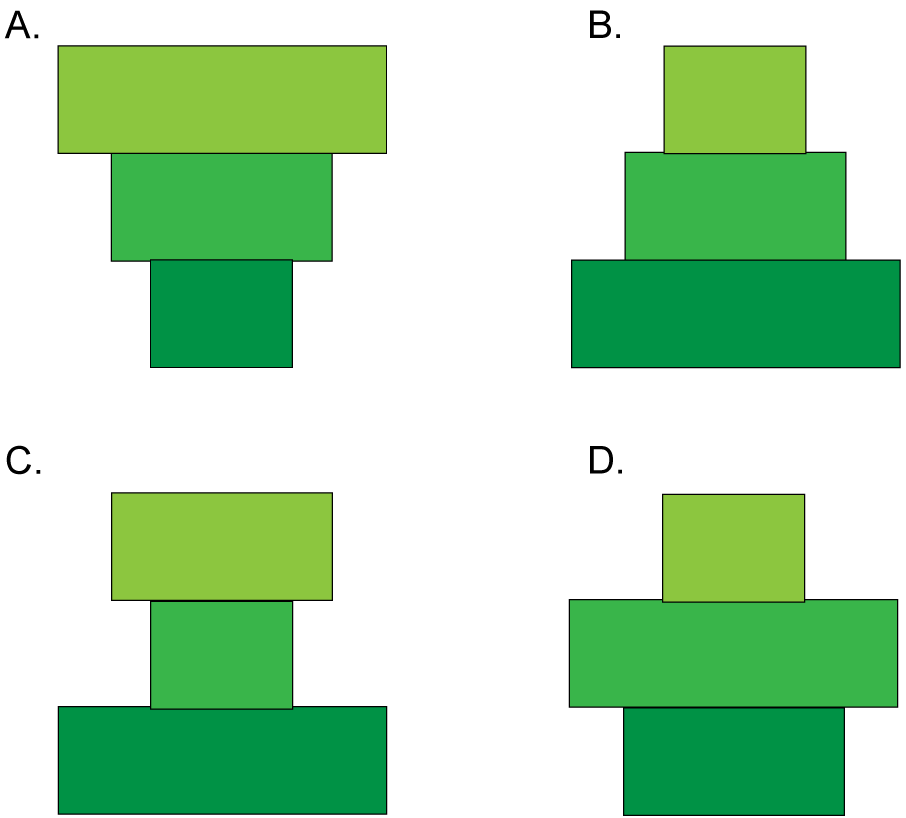
| 8. In a garden, each rose bush provides food for numerous aphids. The aphids are eaten by green lacewings insects as shown by the food chain below.
Rose bush → Aphids → Green Lacewings Which pyramid of energy below accurately represents this relationship? |
||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||
9. Iron-oxidising bacteria are chemoautotrophs that utilise chemiosmosis to produce ATP. Which of the following statements accurately describes this process?
|
||||||||||||||||
10. GPP (gross primary productivity) is the total biomass accumulated by plants in photosynthesis. NPP (net primary productivity) is the GPP minus the biomass lost due to respiration (R) of plants. The diagram below shows the relationship between GPP NPP and R for a particular ecosystem.
If the efficiency of the transfer of energy from GPP to NPP for this ecosystem is 40%, which option is correct for the missing values of NPP and R? |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||