10 questions in 10 minutes |
Q1-2: The image shows two stage of mitosis cell division:
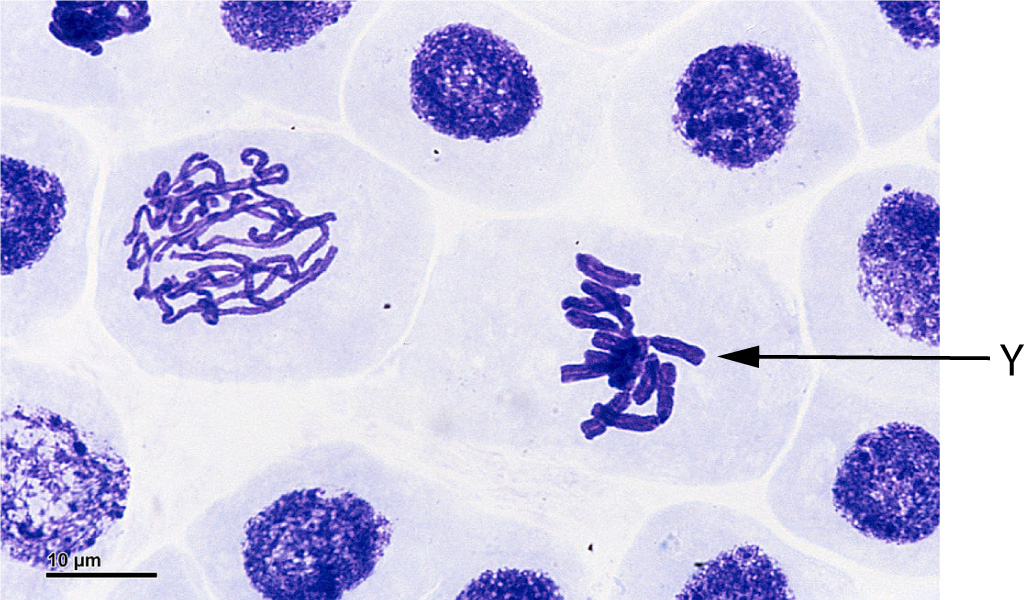
|
Doc. RNDr. Josef Reischig, CSc.
CC-BY-SA 3.0
(label added) |
1. Which stage occurs before stage Y shown in the diagram?
- A. Prophase
- B. Metaphase
- C. Anaphase
- D. Telophase
|
|
2. In the cell Y, sister chromatids are
...
- A. separating
- B. joined together
- C. doubling in size
- D. halving in size
| |
3. What are the correct characteristics of cytokinesis?
| I. Cytokinesis is division of all organelles in the cell |
| II. Both daughter cells must receive at least one mitochondrion and organelles that can only be produced by dividing a pre-existing structure. |
| III. Oogenesis in human is an example of unequal cytokinesis |
|
- A. I and II only
- B. II and III only
- C. I, II, and III
- D. I and III only
|
|
4. Which process occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
- A. Attachment of spindle fibres to the centromeres of each chromosome
- B. Movement of homologous chromosomes to opposite ends
- C. Replication of DNA prior to the start of cell division
- D. Condensation and movement of chromosomes to opposite poles
|
|
5. In meiosis the nucleus undergoes two divisions. Which of the statements about meiosis I is correct?
- A. The number of chromatids is doubled, and the number of chromosomes halved.
- B. The number of chromosomes is halved, and the number of nuclei is doubled.
- C. The number of chromatids is doubled, and the number of chromosomes doubles.
- D. The number of nuclei is halved, and chromosomes is doubled.
|
|
6. Which of the following shows the correct sequence for the cell cycle?
- A. Mitosis → G1 → S → G2 → Cytokinesis
- B. G1 → S → Mitosis → G2 → Cytokinesis
- C. G1 → S → G2 → Mitosis → Cytokinesis
- D. Cytokinesis → Mitosis → G1 → S → G2
| |
7 In which stage of the cell cycle are the cell organelles duplicated?
- A. Prophase of mitosis
- B. G1
- C. G2
- D. S
|
|
8. Which of the following control the cell cycle?
| I. Checkpoints |
| II. Cyclins |
| III. Enzymes |
|
- A. I only
- B. I and II only
- C. II and III only
- D. I, II and III
|
|
9. Which of the following may result in uncontrolled cell division?
| I. Conversion of oncogenes to proto-oncogenes |
| II. Mutations in tumour suppressor genes |
| III. De-activation of telomerase enzyme |
|
|
- A. I only
- B. II only
- C. I and II only
- D. II and III only
| |
10. Which of the following correctly compares benign and malignant tumours?
- A. Benign tumours have a high capacity for metastasis and invasion of neighbouring tissue, while malignant tumours do not.
- B. Both malignant and benign tumours exhibit increased rates of cell division and growth
- C. Benign tumours can invade neighbouring tissues and metastasize to distant sites, while malignant tumours remain localized.
- D. Malignant tumours are generally slow-growing and exhibit low rates of cell division, while benign tumours grow rapidly.
|
|
|