| Triple science: iGCSE Chemistry Only |
|
Q1-2:
The energy level diagram for a reaction with and without a catalyst is shown below:
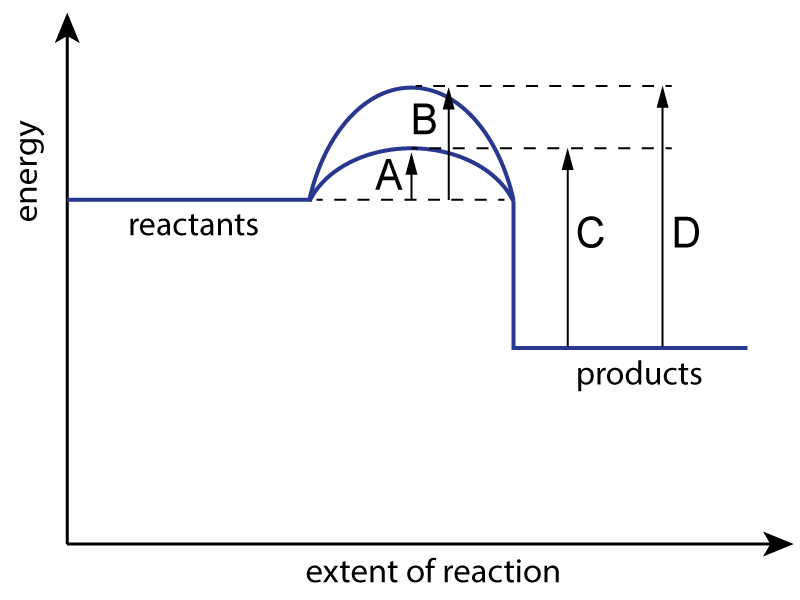
|
|
| 1. Which letter represents the activation energy for the uncatalysed reaction? |
|
| 2. Which letter represents the activation energy for the catalyzed reaction? |
|
Q3-4:
An energy level diagram for a reaction is shown here:

3. Which type of energy change does this diagram represent and what sign should ΔH be given? |
|
| |
Type of change |
Sign of ΔH |
| A |
exothermic |
positive |
| B |
exothermic |
negative |
| C |
endothermic |
positive |
| D |
endothermic |
negative |
|
|
4.For which reaction(s) would this be an appropriate diagram?
| I. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O |
| II. C + O2 → CO2 |
| III. 2H2+ O2 → 2H2O |
|
|
- A. all of them
- B. I and II only
- C. II and III only
- D. none of them
|
|
5. Which of the following statements about catalysts are true? A catalyst..
| I. provides an alternative pathway with lower activation energy |
| II. provides an alternative pathway with a lower enthalpy change |
| III. is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction |
|
|
- A. I and II
- B. I and III
- C. II and III
- D. all of them
|
|
6. Which of the following is correct about the energy changes involved during bond breaking and bond making?
| |
Bond breaking |
Bond making |
| A |
exothermic |
endothermic |
| B |
exothermic |
exothermic |
| C |
endothermic |
endothermic |
| D |
endothermic |
exothermic |
|
|
7. For the reaction:
R2 + S2 → 2RS
Which combination of bond strengths would produce the most exothermic reaction?
| |
Bond strength in R2 and S2 |
Bond strength in RS |
| A |
weak |
weak |
| B |
weak |
strong |
| C |
strong |
weak |
| D |
strong |
strong |
|
|
Q8-10:
The following equation represents the conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide:
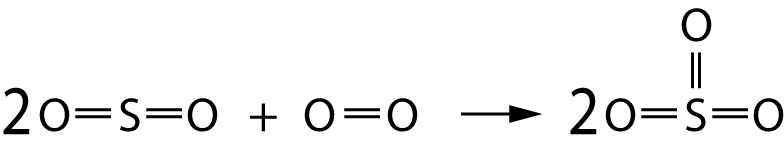
Average bond energies for the bonds involved are:
O=O bond 496 kJ/mol
S=O bond 523 kJ/mol |
|
8. The energy required to break the bonds in the reactants is..
- A. 1542 kJ/mol
- B. 1569 kJ/mol
- C. 2588 kJ/mol
- D. 3138 kJ/mol
|
|
9. The energy given out when the bonds in the products form is..
- A. 1542 kJ/mol
- B. 1569 kJ/mol
- C. 2588 kJ/mol
- D. 3138 kJ/mol
|
|
10. The enthalpy change, ΔH, for this reaction is..
- A. +550 kJ/mol
- B. -550 kJ/mol
- C. +27 kJ/mol
- D. -27 kJ/mol
|
|
|