| Target: 10 Questions in 10 minutes An IB Physics data booklet is helpful |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Q1-5: A tennis ball - initially at rest - is dropped from a height of 5 m. Air resistance is negligible as it falls.
|
|
||||||||||||||||
1. Which of these answers correctly labels the letters 's', 'v' and 'u' in the 'suvats' equations?
|
|||||||||||||||||
2. Which of these answers correctly gives the approximate values for 's', and 'u' and 'a' in the 'suvats' equations? (No units are given).
|
|||||||||||||||||
3. Which of these equations can be used without further calculation to find the impact velocity?
|
|||||||||||||||||
4. What is the impact velocity of the ball?
| |||||||||||||||||
5. How long did it take for the ball to fall to the ground?
| |||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
6. What is the final velocity of the ball?
|
|||||||||||||||||
7. How far does the ball roll in this time?
|
|||||||||||||||||
8-10. A stone is thrown horizontally at 10 ms-1 from a cliff of height 5 m. Air resistance can be ignored.
|
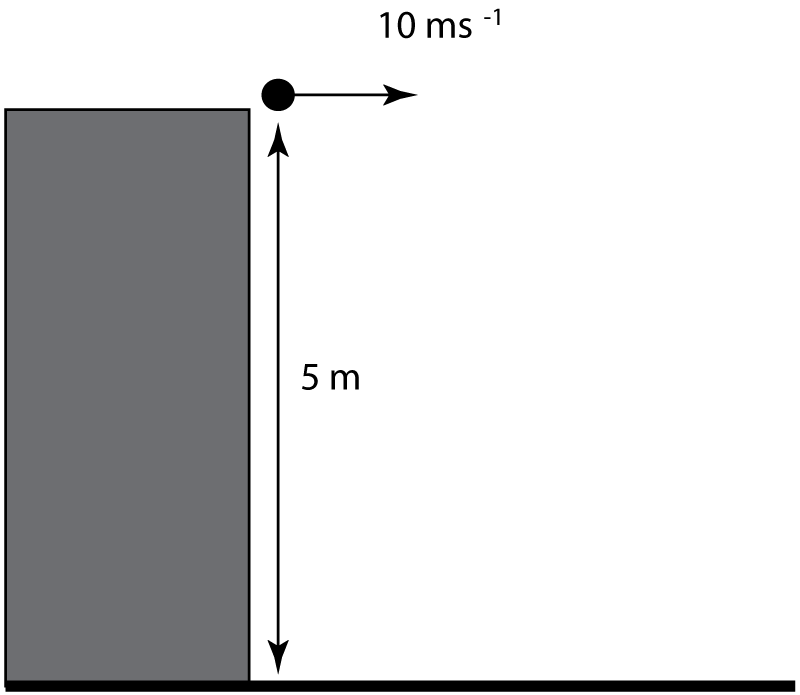 |
||||||||||||||||
8. Which of these correctly describes the changes in the horizontal and vertical components of velocity of the stone?
| |||||||||||||||||
9. What is the vertical velocity of the stone on impact?
| |||||||||||||||||
10. The stone takes 1 second to reach the ground. How far from the cliff edge does the stone land?
| |||||||||||||||||
Question 1:
The letters in the suvat equations (which are used to solve problems involving motion with constant acceleration) represent:
s = displacement
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
a = constant acceleration
t = time
The correct answer is D.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 2:
Explanation of SUVAT values for a dropped object
Defining the variables
s is the displacement, which is the change in position.
u is the initial velocity.
v is the final velocity.
a is the acceleration.
t is the time.
Analysis of the problem
s: The ball is dropped from a height of 5 m, so the displacement s is 5 m.
u: The ball is initially at rest, meaning its initial velocity u is 0.
a: The ball is under the influence of gravity. The acceleration due to gravity, a, is approximately 10 m/s2. The problem states that air resistance is negligible, so the only force acting on the ball is gravity.
The correct answer is C. The values for s, a, and u are 5, 10, and 0 respectively.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 3:
Explanation of SUVAT equations
To find the final velocity without any further calculations, you need an equation that relates the known values to the unknown value you are trying to find.
Knowns:
Initial velocity () is 0 m/s because the ball is dropped from rest.
Displacement () is 5 m.
Acceleration () is approximately due to gravity.
Time () is unknown. * Analysis of the equations:
A. : This equation includes time (), which is an unknown variable. Therefore, you cannot use this equation without first calculating the time it takes for the ball to fall.
B. : This equation solves for displacement (), and it also includes time (). Since displacement is already known and time is not, this is not the correct equation to use.
C. : This equation relates final velocity () to the known variables of initial velocity (), acceleration (), and displacement (). Because all the variables on the right side of the equation are known, you can directly solve for the final velocity ().
D. : This equation solves for displacement () and includes the unknown variable, time (). Thus, it is not the correct equation to use.
Therefore, the only equation that can be used to find the impact velocity directly,
without needing to calculate time first, is .
The correct equation is C. .
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 4:
Using the kinematic equation , where:
is the final velocity (what we need to find)
is the initial velocity, which is because the ball is at rest
is the acceleration due to gravity, approximately
is the displacement, which is
We can substitute these values into the equation:
To find the final velocity, take the square root of both sides:
The calculated impact velocity is , which matches option B.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 5:
Calculation
To find the time it took for the ball to fall, we can use the kinematic equation s=ut+½at 2 .
s is the displacement, which is 5 m.
u is the initial velocity, which is 0 m/s because the ball was at rest.
a is the acceleration due to gravity, approximately 10 m/s2 .
t is the time we want to find.
Substitute the known values into the equation:
5=(0)t+
½(10)t2
5=5t2
Now, solve for t:
t2=1
so t=1s
The calculated time is 1s, which corresponds to option C.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 6:
Calculation
To find the final velocity of the ball, we can use the kinematic equation v=u+at.
v is the final velocity (what we need to find).
u is the initial velocity, which is 2 m/s.
a is the acceleration, which is 4 m/s2 .
t is the time, which is 5 s.
Substitute the known values into the equation:
v=2+(4)(5)
v=2+20
v=22 m/s
The calculated final velocity is 22 m/s, which matches option B.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 7:
To find how far the ball rolls, we can use the kinematic equations s = ut + ½at2.
is the displacement (what we need to find).
is the initial velocity, which is .
is the acceleration, which is .
is the time, which is .
Substitute the known values into the equation:
The calculated displacement is , which matches option D.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 8:
In projectile motion, such as a stone thrown horizontally from a cliff, the horizontal and vertical motions are independent of each other.
Horizontal Velocity: There is no force acting on the stone in the horizontal direction (since air resistance is negligible), so there is no horizontal acceleration. According to Newton's first law of motion, an object will maintain a constant velocity if no force acts upon it. Therefore, the horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the stone's flight.
Vertical Velocity: The only force acting on the stone is gravity, which pulls it downward. This force causes the stone to accelerate downwards at a rate of approximately (the acceleration due to gravity). The initial vertical velocity is zero since the stone is thrown horizontally, but as it falls, its vertical velocity continuously increases.
The correct answer is A. The horizontal velocity remains constant, while the vertical velocity increases.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 9:
Calculation
To find the vertical velocity of the stone on impact, we need to consider only the vertical component of the motion. We can use the kinematic equation v2 = u2 + 2as for the vertical direction.
v is the final vertical velocity (what we need to find).
u is the initial vertical velocity, which is 0 m/s because the stone is thrown horizontally.
a is the acceleration due to gravity, approximately 10 m/s2.
s is the vertical displacement, which is 5 m.
Substitute the values into the equation:
v2 =(0)2+2x10x5
v2=0+100
v2 =100
To find the final vertical velocity, take the square root of both sides:
v=
sqrt100
v=10 m/s
The calculated final vertical velocity is 10 m/s, which matches option B.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 10:
Calculation
To find the horizontal distance the stone travels, we only need to consider the horizontal motion. Since air resistance is ignored, the horizontal velocity remains constant. The formula for distance is:
distance=velocity x time
Horizontal velocity is 10 m/s.
Time is 1 s.
Distance =10 m/s x 1 s
Distance =10 m
The stone lands 10 m from the edge of the cliff.
The correct answer is A, 10 m.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.