|
Target: 10 Questions in 10 minutes |
|||||||||||||||||
1+2: These questions are about friction: |
|||||||||||||||||
1. The symbol µs in the IB data book refers to the quantity..
|
|||||||||||||||||
2. If µd is equal to 0.5, this means that the maximum force produced by friction on a moving object is half the size of ..
|
|||||||||||||||||
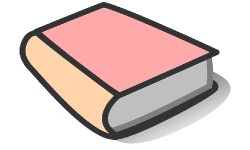
3-5. A book of mass 1.0 kg rests on a rough horizontal surface with µs= 0.4.
|
 |
||||||||||||||||
3. What is the approximate value of the normal force (reaction) on the book?
|
|||||||||||||||||
4. What is the maximum frictional force preventing the book moving to the left or right if pushed?
| |||||||||||||||||
5. The horizontal surface is raised at one end so that the book rests on a slope. It remains stationary. What happens to the sizes of the normal force (reaction) and the maximum force of static friction as the surface is lifted at one end?
| |||||||||||||||||
6. This large cruise liner has a very high mass. It also displaces a large volume of water. When floating in the ocean, which of the following statements is true? |
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
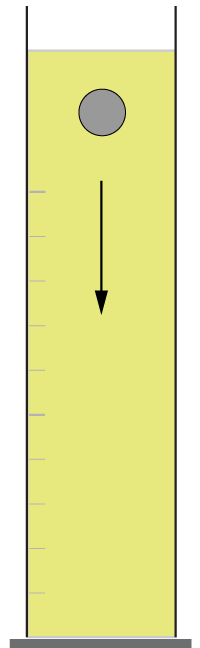
7-10: A student is investigating how the radius r of an aluminium ball affects the terminal velocity when falling through oil. The ball is acted on by several forces including the weight of the ball W, a boyancy force Fb and a viscous force Fv. |
 |
||||||||||||||||
7. If the radius of the steel ball is doubled, what affect does this have on W and Fb?
| |||||||||||||||||
8. When falling through the oil at terminal velocity, which of these statments is true?
| |||||||||||||||||
9. The ball eventually rests on the bottom of the cylinder. If the volume of the ball is V, and the density of the oil is ρoil then the normal force FN from the cylinder base acting on the ball is:
| |||||||||||||||||
10. The ball is changed to a different material of the same radius but with 3 times the density.
| |||||||||||||||||
Question 1:
The symbol μs represents the coefficient of static friction. This dimensionless quantity describes the ratio of the maximum force of static friction (Fs) to the normal force (N) pressing two surfaces together. The formula is:
Fs ≤μs N
The coefficient of static friction (μs) is a measure of how much friction exists between two surfaces that are not moving relative to each other.
The correct answer is B. the coefficient of static friction.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 2:
The coefficient of dynamic (or kinetic) friction, μd, represents the ratio between the force of kinetic friction and the normal force. The formula is:
Fd = μd N
Where:
Therefore, if μd =0.5, it means that the force of friction is half the size of the normal force, or Fd =0.5×N. This relationship holds true regardless of the object's weight, driving force, or air resistance. The normal force is the perpendicular force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it.
The correct answer is C. the normal force (reaction) of the surface on the object.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 3:
Normal Force on the book
The book is resting on a horizontal surface, which means there are no vertical forces other than its weight and the normal force from the surface. Since the book is not accelerating vertically, the normal force must be equal in magnitude to its weight.
Weight (W) is calculated using the formula W=mg.
m=1.0 kg
Use g≈10 N/kg for simplicity.
W=1.0 kg×10 N/kg
=10 N.
Therefore, the Normal Force (N) is approximately 10 N. This corresponds to answer C.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 4:
Maximum frictional force
The maximum static frictional force (Fs,max) is calculated by multiplying the coefficient of static friction (μs) by the normal force (N).
Fs,max=μs ×N
μs =0.4
N=10 N
Fs,max=0.4×10 N=4 N.
This is the maximum force that can be applied before the book begins to slide.
This corresponds to answer D.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 5:
Forces on an inclined slope
When the horizontal surface is raised to form a slope, the normal force and the maximum static frictional force both change.
Normal Force: The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. As the slope's angle (θ) increases, the component of the book's weight that is perpendicular to the surface decreases. The formula for the normal force on a slope is N=mgcosθ. Since cosθ decreases as θ increases from 0 to 90 degrees, the normal force also decreases.
Maximum Static Frictional Force: The maximum static frictional force is directly proportional to the normal force Fs,max=μs ×N. Since the normal force is decreasing as the slope is lifted, the maximum static frictional force also decreases.
This corresponds to answer A.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 6:
The correct statement is C. The weight of water displaced is equal to the total weight of the boat.
Archimedes' Principle
This is a direct application of Archimedes' principle, which states that the buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces. For an object to float, the buoyant force must be equal in magnitude to the object's total weight.
Weight of water displaced is the buoyant force.
The buoyant force must be equal to the total weight of the boat for it to float in equilibrium.
Here is a breakdown of the other options:
A and B are incorrect because they focus on the mass or weight of the portion of the boat that is underwater, not the total mass or weight. The principle applies to the entire object.
D is incorrect because the volume of water displaced is only equal to the volume of the part of the boat that is submerged below the waterline, not the total volume of the boat.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 7:
The correct answer is D. 8 times larger, 8 times larger.
When the radius of a spherical object is doubled, both its weight and the buoyancy force acting on it increase by a factor of 8. This is because both forces are directly proportional to the volume of the sphere.
Weight (W)
The weight of the ball is given by the formula W=mg, where m is the mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The mass is the density of the aluminum (ρ) multiplied by the volume of the ball (V).
m=ρ x V
The volume of a sphere is given by the formula V= 4/3 πr3 Substituting the volume into the weight equation:
W=ρ 4/3 πr3 . g
If the radius (r) is doubled to 2r, the new weight (W') will be:
W'=ρ
4/3 π(2r)3 . g
W'=ρ
4/3 π 8 r3 . g
W'=8W
The weight becomes 8 times larger.
Buoyancy Force (Fb)
According to Archimedes' Principle, the buoyancy force is equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. The volume of the displaced fluid is the same as the volume of the ball itself.
Fb=weight of displaced fluid=ρ 4/3 πr3. g
If the radius (r) is doubled to 2r, the new buoyancy force Fb' will be:
Fb' =ρ
4/3 π(2r)3 . g
Fb'=ρ
4/3 π 8 r3 . g
Fb'= 8Fb
The buoyancy force also becomes 8 times larger.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 8:
Explanation
When the ball reaches terminal velocity, it means that its acceleration is zero. According to Newton's First Law of Motion, this occurs when the net force acting on the object is zero, i.e., all the forces are balanced.
The forces acting on the falling ball are:
For the forces to be balanced, the total upward force must be equal to the total downward force.
Downward force: W
Upward forces: Fb+Fv
Therefore, at terminal velocity, the sum of the upward forces equals the downward force:
W=Fb+Fv
The correct statement is A. The forces are balanced, and W = Fv + Fb.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 9:
When the ball is at rest on the bottom of the cylinder, the forces on it are balanced. The downward force (the ball's weight) is equal to the sum of the upward forces (the buoyancy force and the normal force from the bottom of the cylinder).
Downward Force:
The only downward force is the ball's weight, W.
W=mg
Upward Forces:
The buoyant force (FB) is the upward force exerted by the oil on the ball. According to Archimedes' principle, this force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the ball.
FB =weight of displaced oil=(density of oil)×(volume of ball)×g
FB = ρoilV g
The normal force (FN) is the force exerted by the bottom of the cylinder on the ball.
Equilibrium Equation:
Since the ball is not moving, the forces are in equilibrium:
Total Downward Force = Total Upward Force
W=FB + FN
Solve for the Normal Force:
mg=ρoilV g + FN
FN = mg - ρoilV g
Factor out g:
FN = g (m - ρoilV)
The correct answer is C. FN = g(m−ρoilV).
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.
Question 10:
When a ball of the same radius but with 3 times the density is used, its terminal velocity increases. Here's why:
At terminal velocity, the downward force (weight, W) is balanced by the upward forces (buoyancy force, Fb
, and viscous drag force, Fv).
W=Fb+Fv
The buoyancy force (Fb) is dependent on the volume of the ball and the density of the fluid. Since the radius (and thus volume) of the ball is unchanged, the buoyancy force remains the same.
The weight (W) is given by W=mg, which can be written as W=ρVg. Since the density of the ball is 3 times greater and the volume (V) is the same, the weight is 3 times larger.
With a larger downward force and the same upward buoyancy force, a greater viscous drag force is required to achieve a balance and reach terminal velocity.
The viscous drag force (Fv) depends on the velocity of the ball. The exact relationship can vary, but for many objects falling at moderate speeds in a fluid like oil, drag is proportional to velocity (Fv∝v). Since a larger drag force is needed to balance the increased weight, the terminal velocity must increase.
W'
=Fb + Fv'
3W=Fb + Fv'
Since W>Fb , the new drag force Fv' ) must be significantly larger than the old drag force (Fv ), which means the new terminal velocity must be higher.
The correct answer is C. Terminal velocity increases.
*These A.I. responses have been individually checked to ensure they match the accepted answer, but explanations may still be incorrect. Responses may give guidance but the A.I. might not be able to answer the question! This is particularly the case for questions based on diagrams, which the A.I. typically cannot interpret.
Grade Gorilla uses Gemini, Deepseek and a range of other A.I. chatbots to generate the saved responses. Some answers have had human intervention for clarity or where the A.I. has not been able to answer the question.